1. Definition of Diabetes Disease
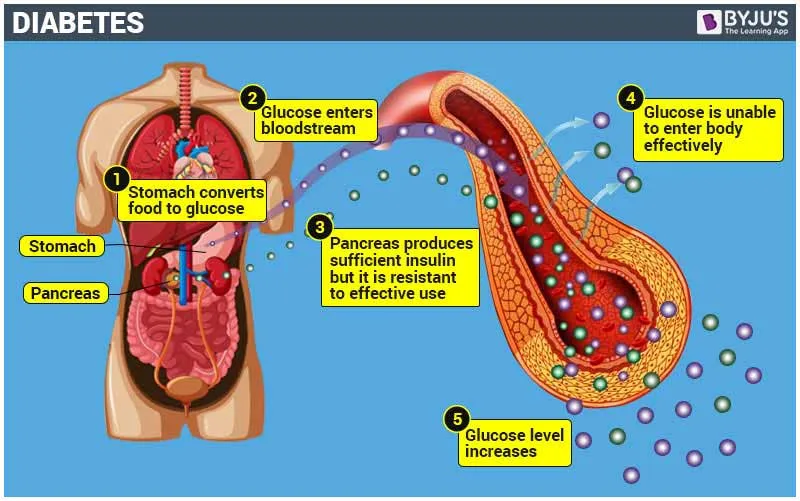
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. It involves issues with the hormone insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. When your body doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it makes, it leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which can cause various health complications. Diabetes is a significant global health concern, affecting millions worldwide. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and management strategies for diabetes is crucial for prevention and treatment.
2. Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, each with different causes and characteristics:
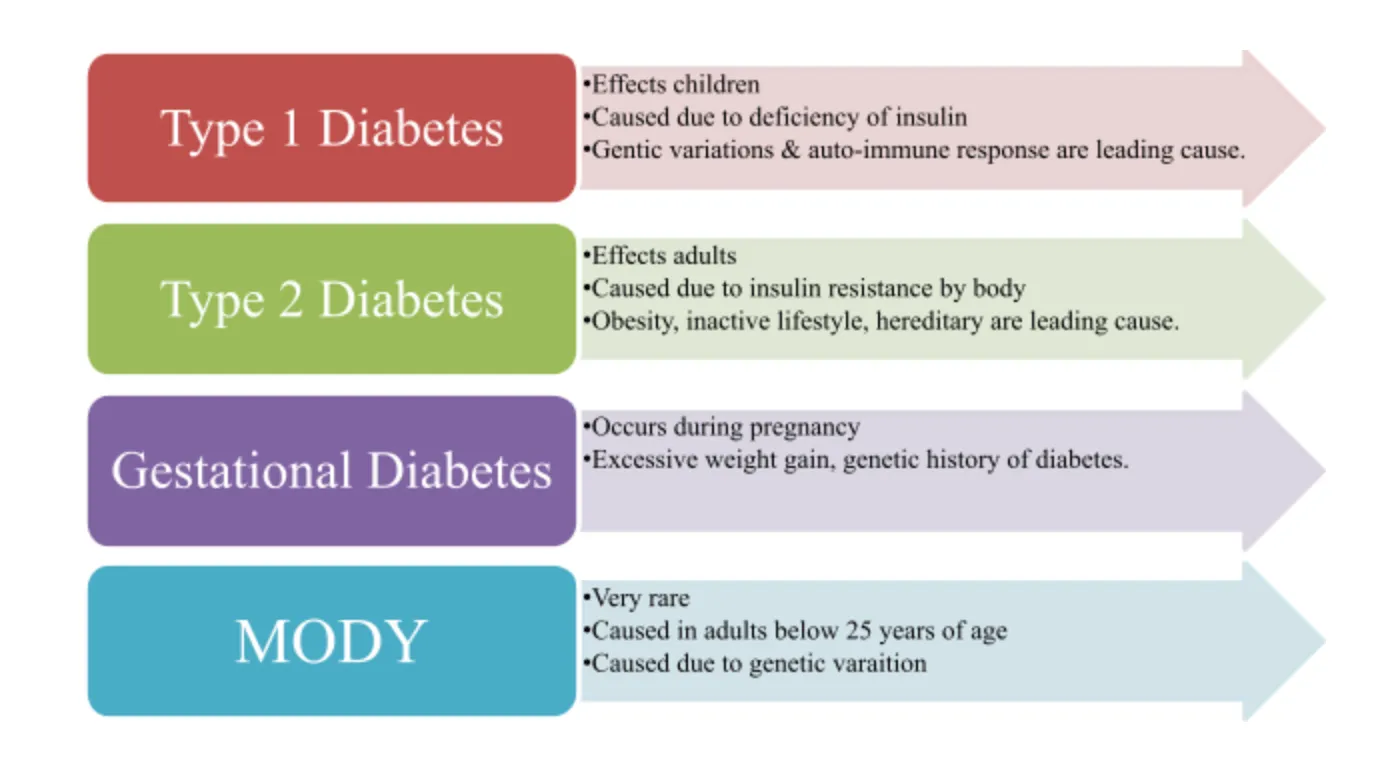
- Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It is typically diagnosed in children and young adults, making them dependent on insulin for life.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form of diabetes, Type 2, is characterized by insulin resistance. The body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively. This type is largely associated with lifestyle factors, such as obesity and lack of exercise.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. However, it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Prediabetes: A condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as Type 2 diabetes. Early detection and lifestyle changes can prevent the progression to full-blown diabetes.
3. Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of diabetes vary depending on the type:
- Genetic Factors: Family history plays a significant role, particularly for Type 2 diabetes.
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet high in sugars and refined carbs, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle are major contributors to Type 2 diabetes.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain toxins or viruses might trigger Type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Other Factors: Stress, hormonal changes, and the use of certain medications can also increase the risk.
4. Symptoms of Diabetes
Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent urination and increased thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can appear suddenly, whereas Type 2 diabetes symptoms may develop slowly over time and might not be noticeable initially.
5. Diagnosis of Diabetes
Diabetes can be diagnosed through several types of blood tests:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar levels after fasting overnight.
- Hemoglobin A1C Test: Provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Measures blood sugar levels before and after consuming a sugary drink.
Regular screening is crucial, especially for those at high risk of developing diabetes.

6. Management and Treatment of Diabetes
Effective management of diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, monitoring, and medication:
- Lifestyle Modifications: A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management are essential. Foods with low glycemic index (GI) are recommended to help manage blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Insulin therapy is essential for Type 1 diabetes. For Type 2 diabetes, medications like Metformin can help control blood sugar levels.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regular monitoring using blood glucose meters or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) helps manage diabetes effectively.
- Healthcare Support: Regular consultations with healthcare providers, including dietitians and endocrinologists, are essential for optimal management.
7. Role of Supplements in Diabetes Management
Supplements can play a supportive role in managing diabetes, especially when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise. Common supplements include:
- Chromium: May improve insulin sensitivity and help manage blood sugar levels.
- Magnesium: Essential for many body processes, including blood sugar regulation.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): An antioxidant that can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce symptoms of diabetic neuropathy.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Help reduce inflammation and support heart health, which is crucial for diabetics.
- Berberine: Has been shown to lower blood glucose and improve lipid metabolism.
- Cinnamon: Some studies suggest it may help lower blood sugar levels, though more research is needed.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement, as they can interact with medications and other health conditions.
8. Diet and Nutrition for Diabetics
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes:
- Understanding the Glycemic Index (GI): Foods with a low GI are absorbed more slowly and cause a slower rise in blood sugar levels.
- Nutritional Recommendations: A diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and high-fiber foods is recommended. Reducing intake of refined sugars and processed foods is also crucial.
- Meal Planning Tips: Regular, balanced meals help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Portion control and meal timing are important for managing diabetes effectively.

9. Complications of Uncontrolled Diabetes
If not managed properly, diabetes can lead to serious complications:
- Short-term Complications: Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
- Long-term Complications: Cardiovascular disease, nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney damage (nephropathy), eye damage (retinopathy), and foot problems due to poor circulation and nerve damage.
10. Preventing Diabetes
Prevention focuses on lifestyle changes:
- Lifestyle Interventions: Adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise routine can prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
- Early Intervention and Education: Raising awareness and providing education about diabetes can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices to reduce their risk.
11. Living with Diabetes
Managing diabetes effectively is key to maintaining quality of life:
- Emotional and Psychological Impact: Living with a chronic condition can be challenging, and support from counseling and support groups can be beneficial.
- Daily Management Tips: Establishing a routine that includes medication, diet, exercise, and stress management helps keep diabetes under control.
12. In Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex condition, but with the right management and support, individuals can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. A holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, medical care, and possibly supplements can help manage diabetes effectively. Awareness, education, and early intervention remain crucial in preventing and managing this global health issue.




 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.